a multi-account/subscription/project structure for segregated environments and workloads
Abstract
This article provides an introduction to Cloud Landing Zones, explaining their importance as a foundation for cloud adoption. It outlines key design principles to guide effective implementation, highlights crucial architectural considerations, and showcases our expertise in delivering tailored solutions. Additionally, it presents a real-case example of a GCP (Google Cloud Platform) Landing Zone implementation, offering practical insights from a live insurance project. Whether you are just beginning your cloud journey or optimizing an existing setup, you will find valuable lessons to support your goals.
Partnership with major cloud providers (Google Cloud, AWS, Microsoft Azure).
Extensive experience in designing and implementing robust landing zones, aligning technical architecture with business goals.
Overview of successful implementation of a scalable GCP (Google Cloud Platform) Landing Zone for a leading UK insurer.
Cloud Landing Zones – Stable Foundation for Cloud Transition
Cloud adoption is a complex process that requires many elements to be in the right place for a successful transformation. Organisations need an environment where they can test and validate their cloud strategy before going live. It can be achieved thanks to Cloud Landing Zones, which serve as a secure sandbox for experimenting and launching solutions created by your team. As the insurance companies increasingly move to cloud computing, they should see it as a starting point for a secure and efficient transition that will play crucial role for further development.
What is a Cloud Landing Zone?
A Cloud Landing Zone is a pre-configured, secure, and scalable setup for organisations moving their IT resources to the cloud. Essentially, it’s a structured “starting point” that simplifies cloud adoption by addressing key concerns such as governance, scalability, and operational efficiency. By creating a well-prepared Cloud Landing Zone, organisations can reduce the time and effort teams need to onboard to the cloud by providing a framework for effective collaboration without compromising on control or security. This approach lays a reliable foundation to help manage cloud resources more consistently, avoid misconfigurations, and enforce essential security and compliance standards.
While the exact configuration of a Landing Zone will vary by the Cloud Service Providers (CSP), an effective Cloud Landing Zone includes several critical elements:
manage risk of unproper handling of automated financial transactions
robust identity and access management (IAM)
Importance of Cloud Landing Zone for Financial Companies
For regulated industries with strict compliance requirements, such as insurance, Cloud Landing Zones are invaluable. They build regulatory safeguards into the infrastructure from the start. Automated guardrails enforce data protection, access control, and logging policies, enabling these organisations to navigate complex compliance demands while safely adopting cloud technologies.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Insurance firms handle large volumes of sensitive data, from personal customer information to financial records. A Cloud Landing Zone strengthens security through features such as data isolation and segmentation, ensuring unauthorised access is minimised. This is critical for maintaining customer trust and compliance with industry standards.
Regulatory compliance, a major concern for insurance companies, becomes more manageable with pre-configured policies embedded in landing zones. Cloud providers often include templates for regulations such as GDPR or other regional frameworks, ensuring firms can meet requirements with minimal manual intervention.
Streamlined Operations for Multi-Account Environments
Insurance companies often need to manage multiple departments, projects, and geographies. Cloud Landing Zones simplify this by providing scalable, multi-account architectures. For example, an insurer can separate accounts for policy management, claims processing, and customer-facing applications, all while maintaining unified governance.
Automation is another key benefit. Landing zones reduce repetitive tasks, such as setting access permissions or configuring security protocols, allowing IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives. Additionally, by optimising resource allocation, firms can avoid wasted spending and ensure their cloud investments deliver maximum returns.
Accelerated Time-to-Deployment
In the competitive insurance market, speed is of the essence. Cloud Landing Zones enable faster deployment of workloads by providing pre-configured templates and best practices. This reduces the setup time for new environments, ensuring that digital transformation initiatives are rolled out without unnecessary delays. Moreover, these standardised setups minimise the likelihood of configuration errors, improving overall reliability.
Key Principles for Designing a Landing Zone
To properly design a landing zone, insurance firms should adopt a strategic approach:
- Aligning Organization and Cloud: The Landing Zone must consider the organisational structure and established forms of communication and collaboration. However, not all existing practices can be adapted to the dynamics of working in a cloud environment and fully leverage its potential.
- Building with Cooperation in Mind: Find a balance between control and oversight and the flexibility and autonomy of project teams. The security team or cloud platform team will quickly become overwhelmed by requests from project teams if they are unable to deliver.
- Focusing on the Essentials: The Landing Zone should serve as a foundation for project operations, providing essential support, especially for teams with limited cloud experience. It is not intended to address every challenge or meet every need up front. Instead, it should provide a solid foundation that can be expanded and adapted as specific needs arise.
Building an Effective Cloud Landing Zone Architecture
To get most of the cloud benefits, a Cloud Landing Zone should be well-designed and have all the crucial elements in place. Here is how to design an architecture that meets the high demands of the insurance industry:
Define Account and Network Architecture
- Set up Multiple Accounts: Establish accounts/subscriptions/projects (depending on the CSP’s terminology) for specific functions such as production, development, and testing, ensuring that workloads are isolated but interoperable. Insurance companies can create separate accounts for handling sensitive financial data, compliance testing, and customer-facing applications.
- Secure Network Configuration: Segment network traffic similarly to the organizational structure plan IP address ranges in advance. Identify which systems need to communicate with each other and where they are located: on-premises, other clouds, or service providers. This will determine whether peer-to-peer communication is possible or if a hub-and-spoke model should be implemented and what services do you need.
Implement Governance Policies
- Access and Identity Management: Use Identity and Access Management (IAM) to enforce role-based access, ensuring that only authorised users can access sensitive data and applications.
- Organization Polices: Establish the rules, constraints, and limitations to prevent teams from making common mistakes or taking shortcuts.
- Tagging and Resource Organization: Implement tagging policies to organise resources, track usage, and enforce cost management strategies, making it easier to monitor and control cloud spend. Suggest a naming convention to help avoid naming conflicts.
Build Shared Services and Templates
The next step is to prepare shared services that will be used by multiple projects, such as a mechanism for creating backups, auditing changes, or connecting to the on-premises infrastructure. At this stage, the division of responsibilities between the team overseeing cloud usage and the project teams will be refined. This process should take place in an atmosphere of shared responsibility for the proper use of the platform.
Project teams will create solutions that can serve as templates for other projects, such as a standard delivery of serverless functionality with a messaging service. However, this will require the engagement and encouragement of the cloud platform team (CPT) to ensure that the implementation follows best practice and is designed for reusability.
Sollers Consulting – Your Partner in Cloud Transformation
As mentioned the exact implementation may vary depending on the Cloud Service Provider of choice, so successful navigating through the process requires knowledge and experience with specific Cloud Platform. We can take care of this process for you, as Sollers Consulting is an official partner of leading cloud providers including:

Google Cloud - Google Cloud Landing Zone

AWS - AWS Control Tower

Microsoft - Microsoft Azure Landing Zone
We can bring our experience in implementing Cloud Landing Zone and other cloud-based solutions for large enterprises. Our expertise covers not only the technical aspects of building cloud infrastructure, but also aligning it with business goals and ensuring a smooth adoption across teams.
A Showcase of GCP Landing Zone Implementation
We have successfully designed a robust landing zone structure for a leading UK insurer. The project involved creating a well-organised hierarchy of projects and folders in GCP (Google Cloud Platform), defining clear roles and responsibilities, and delegating permissions effectively. We also developed a comprehensive migration plan to transition existing projects into the new structure and prepared Terraform-based Infrastructure as Code (IaC) configurations to automate resource provisioning.
The challenge was to reconcile the client’s organisation with how GCP organisations, folders, and projects are designed to be used, while also ensuring compatibility and feasibility for implementation with Terraform. The biggest mistake would be to try to implement them in a way that goes against the logic and mechanisms established by the CSP and IaC tools. Such an approach could result in configurations becoming deprecated, as customisations and unusual use cases may not be addressed in future platform updates and improvements.
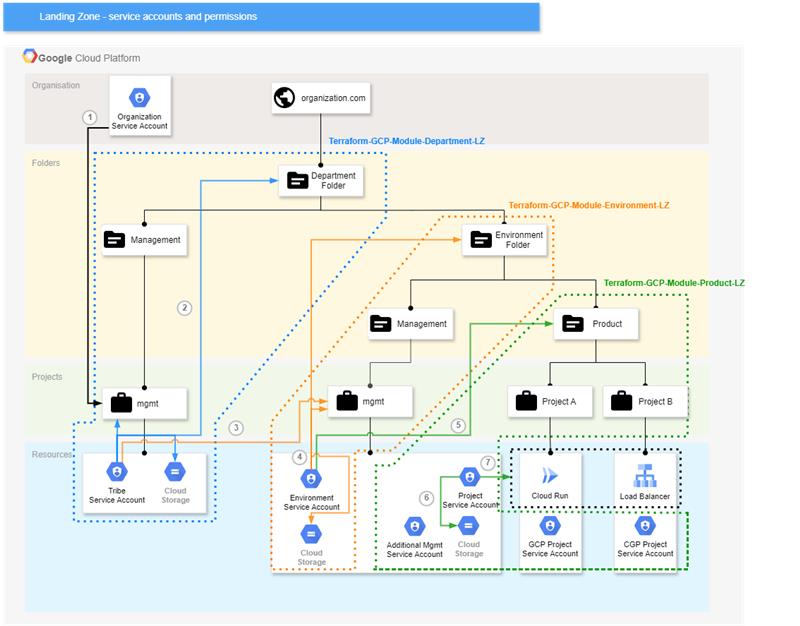
The diagram above illustrates one of the elements we need to design: the organisation of service accounts and their permissions. Note that an integral part of the design is the relationship between GCP resources and the Terraform configuration modules that implement them. Our goal was to achieve a modular approach that would allow these modules to serve as building blocks while still allowing for customisation between Landing Zone deployments for specific projects.
The result was a scalable, tiered architecture that facilitates the efficient addition of new spaces for departments and projects, ensuring both flexibility and long-term sustainability.
Author of the article

Karol Gorecki – DevOps Designer at Sollers Consulting
Karol Gorecki is a DevOps Designer with a strong focus on creating innovative cloud solutions and implementing robust Infrastructure as Code (IaC) configurations. Over his 8-year career at Sollers Consulting, he has worked across the full spectrum of DevOps technologies, combining deep technical expertise in cloud architecture and automation tools with a solid understanding of agile methodologies.
Contact Us



